What are Microorganisms?
A microorganism is an organism also known as Microbe. Microorganism can be bacteria, fungi, archea or protists. The organism is so tiny, it is too small to be seen by the naked eye but visible through a microscope.
Microorganisms were first distinguish by Anton van Leeuwenhoek in 1675
Each type has a characteristic cellular composition, morphology, mean of locomotion, and reproduction.
Microorganisms are beneficial in producing oxygen, decomposing organic material, providing nutrients for plants, and maintaining human health, but some can be pathogenic and cause diseases in plants and humans.
Microorganisms are divided into seven types: bacteria, archaea, protozoa, algae, fungi, viruses, and multicellular animal parasites
Bacteria
A member of a large group of unicellular microorganisms which have cell walls but lack organelles and an organized nucleus, including some which can cause disease.
Microbes are single-cell living beings that are not one or the other plants nor animals. They ordinarily degree a couple of micrometers in length and exist together in communities of millions.
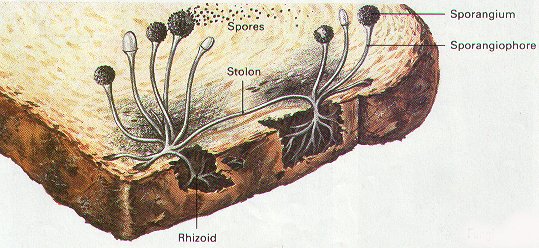
Fungi
Any of a group of spore-producing organisms feeding on organic matter, including mould, yeast, mushrooms, and toadstools.
Fungi is the plural word for "fungus". A fungus is a eukaryotic organism. The study of fungi is called mycology. Like animals, humans and most bacteria, all fungi are heterotrophs. though fungi have abundant a lot of in common with animals than plants, mycology is frequently seen as a branch of botany (plant science).

Archaea
Archaea are prokaryotic cells with enthusiasm to extraordinary natural conditions. In light of their natural surroundings, all Archaeans can be isolated into the accompanying gatherings: methanogens (methane-creating creatures).
They retain daylight utilizing their film color, bacteriorhodopsin. This responds with light, prompting the development of the vitality atom adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
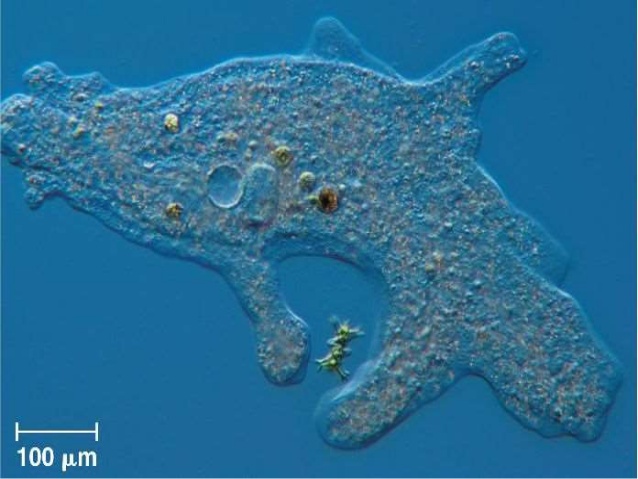
Protozoa
Protozoa are unicellular oxygen consuming eukaryotes. They have a core, complex organelles, and acquire sustenance by retention or ingestion through particular structures. They make up the biggest gathering of living beings on the planet as far as numbers, biomass, and assorted variety.
Their cell dividers are comprised of cellulose. They likewise have diverse methods for nourishment, which bunches them as autotrophs or heterotrophs.
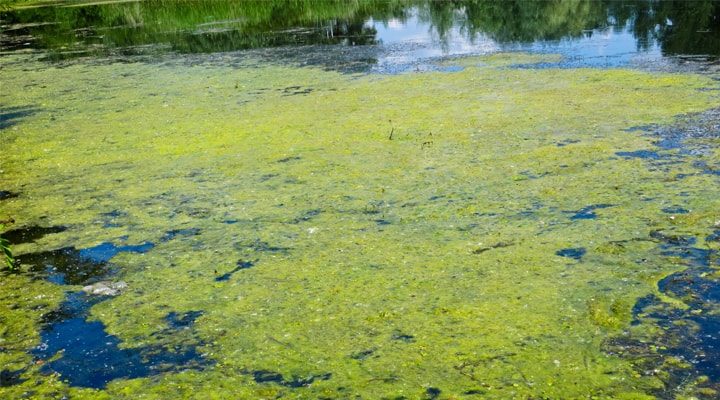

Algae
Algae, additionally called cyanobacteria or blue green growth, are unicellular or multicellular eukaryotes that get sustenance by photosynthesis.
They live in water, clammy soil, and shakes and produce oxygen and starches utilized by different living beings. It is trusted that cyanobacteria are the birthplaces of green land plants.
Viruses
Infections are noncellular elements that comprise of a nucleic corrosive center (DNA or RNA) encompassed by a protein coat.
In spite of the fact that infections are delegated microorganisms, they are not viewed as living beings. Infections can't replicate outside a host cell and can't use individually. Infections regularly overrun prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells causing illnesses.
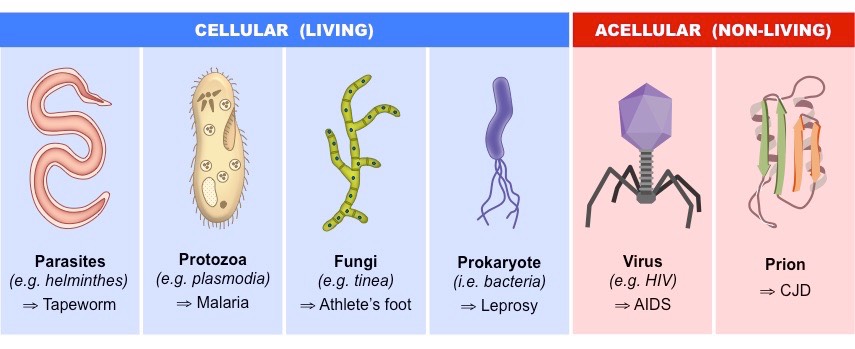
Multi- cellular Animal Parasites
A gathering of eukaryotic living beings comprising of the flatworms and roundworms, which are altogether alluded to as the helminths.
In spite of the fact that they are not microorganisms by definition, since they are sufficiently expansive to be effectively observed with the exposed eye, they carry on with a piece of their life cycle in tiny structure.